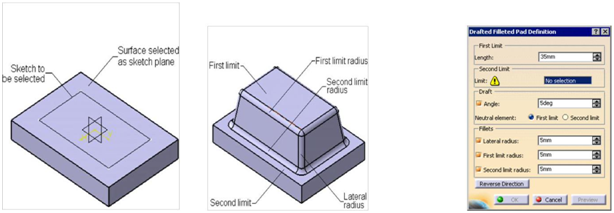
Reference element is the features that have no mass and volume are used
only to assist we in the creation of the models. They acts as a reference for
drawing a sketches for features, defining the sketch plane, placing placed
features, assembling components, creating sketched based feature, and so on.
REFERENCE PLANES
The features are generally not created on a same plane; therefore we
need to select the other defaults planes are creating new planes to be used as
a sketching plane for other feature.
Default Planes :- There are three Default Planes as given bellow:-
1. XY plane
2. YZ plane
3. ZX plane
Creating a new plane
Toolbar: Reference Elements > plane
Planes are used as the sketching plane for drawing sketches for the
sketch-based features, Appling references to the placed features, and so on.
The sketch of the based feature is generally drawn using one of the default
planes as the sketching planes. After creating the based feature, we can select
one of its paces as the sketching plane to draw the sketch for the other-based
features. However sometimes we may need to draw a sketch on a plane, which is
add one offset distance from the planner face of the base feature.
To create a new plane chooses the
plane tool from the reference element (extended) toolbar.
In CATIA V5, There are eleven
different methods for creating new plans as given bellow:-
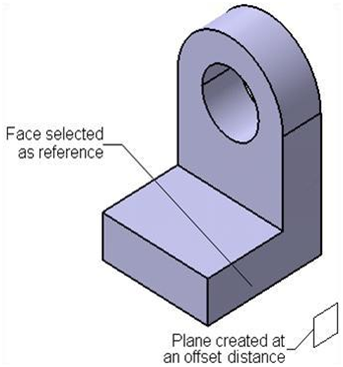
Creating a plane at one offset from an existing plane/planner face
When we invoke the plane definition dialog box and select plane to offset from plane type on
dialog box. Select the plane or the planar face from which the offset plane
need to create now we can set the value of offset distance from the offset
spinner, we can also specify the number copies of the new plane in instance(s)
spinner and then ok.
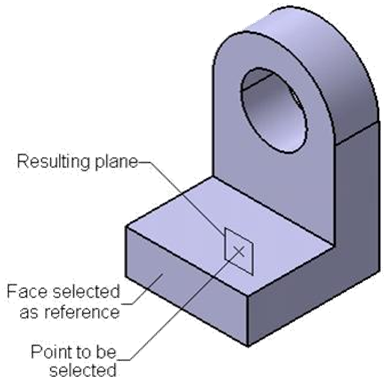
Creating a plane parallel to an existing plane and passing through a
point
The parallel through point
option in the plane type drop down list is used to create an offset plane that
is parallel to reference plane or planar face and passes through specified
point.
To create a plane, select the parallel through point option from the plane
type, select a plane or planar face from the geometry area and select a point.
Select point or vertex from geometry area and then choose OK.
Creating a plane at an angle/normal to a plane
The angle/normal to plane option in the plane type drop–down list is
used to create a plane at an angle to a reference plane or face. We can also
create a plane normal to the selected plane or face. To create a plane using
this option, select the angle/normal to plane option from the plane type
drop-down list; we will be prompted to select the rotation axis. Select an edge
of the model, sketched line, or axis from the geometry area that will be used
as the axis of rotation; we will prompted to select the reference plane. Select
the reference or plane or planar face from the geometry area such that the
rotation axis and the selected reference plane are parallel to each other; the
preview of the plane is displayed set the value of rotation angle in the angle
spinner. To reverse the direction of the plane creation, specify a negative
angular value. Next, choose the ok button from the plane definition dialog box.
If we choose normal to the plane button from the plane definition dialog box, a
plane will be created normal to the reference plane. We can also create
multiple copies of the plane using the repeat object after ok check box. If we
select the project axis on reference plane check box the resultant plane will
be created in the reference plane by projecting the rotation axis over the
reference plane.
Creating a plane through three points
The through three points in a plane type drop down list is used to
create the plane passes through selected points. On selecting this option, we
will be prompted to select the first point Vertex, or an endpoint of a line
from the geometry area. On doing so, we will be prompted to selected the second
point. Select the second point from the geometry area. Similarly select the
third point; choose ok button from the plane definition dialog box the
resulting plane will be displayed.
Creating a plane through lines
The Through Two Lines option
in the plane type drop-down list is used to create a plane that will be passes
through selected lines, edges, or an edge a line. When we select this option we
are prompted to select the first line. Select an edge, sketch line, or an axis
from the geometry
Creating a plane through a point and a line
The Through point and a line
option in the plane type drop-down list is used to create a plane that
passes through a point and a line. When we select this option, we will be
prompted to select this point, we will be prompted to select a point. Select a
point through which we want the plane to pass; we will be prompted to select a
line. Select a line, axis, or edge from the geometry area through which the plane
will pass; the preview of the plane will be displayed in the geometry area.
Choose the Ok button from the plane
definition dialog box.
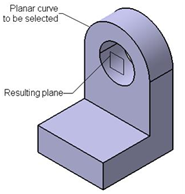
Creating a plane through a planar curve
The Through planar curve option is used to create a plane that will be
coplanar to be selected arc. To create a plane using this option, select the through planar curve option plane type
OK from the plane definition dialog box.
Creating a plane normal to a curve
The Normal to curve option is
used create plane that is normal to a selected curve. On selecting this option,
we will be prompted to select a reference curve. Select the curve from the
geometry area; the preview of the normal plane, placed of the midpoint of
selected curve, is displayed. Note that, by default the midpoint the selected
curve is considered as a point to place the plane normal to curve. If we do not
want create a plane in the middle of the selected curve, select appoint on a
curve/vertex/edge where the plane will be placed. Next, choose the Ok button from the plane definition
dialog box.
Creating a plane using an equation
The equation option is used to create using the equation Ax + By + Cz=D,
where the values of A, B, C, and D are variable and can change to modify the
orientation of the plane. When we select this option the plane definition
dialog box will expand and the A, B, C, and D spinners will be displayed. We
can set the values in these spinners to create a plane using the above
mentioned equation. The normal to compass button in this dialog box is used to
create a plane normal to the compass. The parallel to screen button is used to
create a plane normal to the current view of the screen. After specifying the
parameters, choose the ok button from the plane definition dialog box.
Creating a plane using mean through points
The mean through point option is used to create a plane at an
orientation defined by the mean of the selected points. On selecting this
option, we will be prompted to select points. Select the required points or
vertices from the geometry area. The name of the selected points and vertices
are displayed in the points display box in the plane definition dialog box. The
preview of the plane created with its orientation depending on the mean of the
selected point, is displayed in the geometry area. Choose the Ok button from the plane definition
dialog box.
Create a plane tangent to a surface
The tangent to surface option is used to option create a plane tangent
to selected surface and passing through a selected point. On selecting this
option, we will prompted to select the reference surface. Select a point,
tangent to selected surface, is displayed. Choose ok button from the plane definition dialog box.
THANK YOU,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
FOR MORE INFORMATION please contact facebook